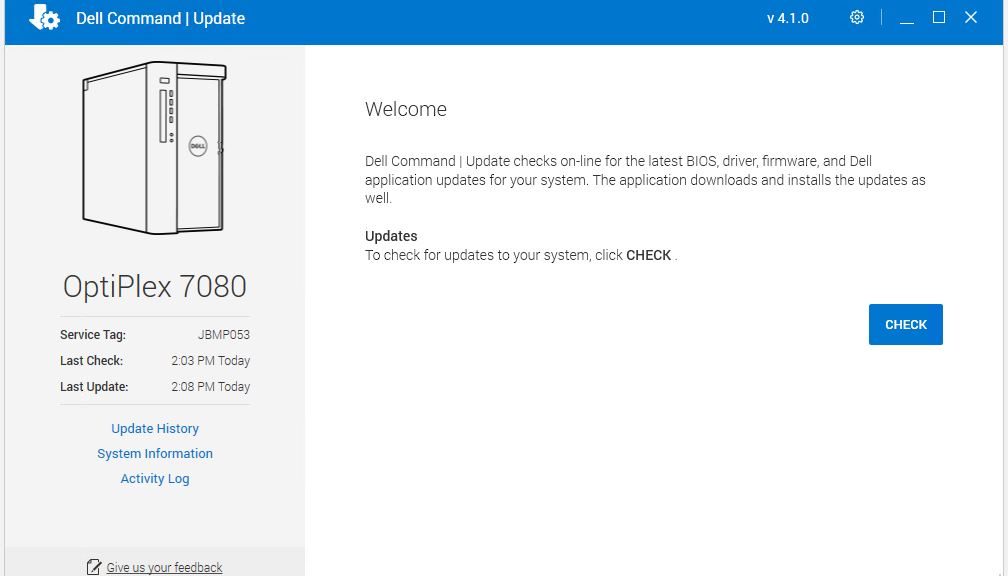
I’ve got a pretty new Dell OptiPlex 7080 Micro SFF PC here at the house. Today, I went through the first BIOS upgrade since I first obtained that machine. When I opine that a Dell BIOS update covers many sins, I mean there was a lot more going on and involved than I expected. The so-called BIOS update was, in fact, 5 updates rolled into one update package. I used the Dell Command | Update utility to handle this, and am climbing its learning curve as well.
How I Learned That Dell BIOS Update Covers Many Sins
At first, because the utility also found a couple of other items to update, I couldn’t get the Command | Update utility to work. Then it dawned on me: perhaps the BIOS update needs to be run by itself? Indeed, that proved to be the ticket to eventual success. It also showed me 5 separate items being updated as the so-called “BIOS Update” was applied:
- BIOS
- USB-C firmware
- Intel Management Engine (IME) firmware
- Primary BIOS EC (Embedded Controller) update
- Backup BIOS EC update
Thus, where I’d been thinking this was a straight-up, in-and-out BIOS update, it was actually a whole bunch of chained updates that included other device controllers, IME, and embedded controllers. Not having a lot of experience in dealing with such updates from Dell lately, this came as a surprise.
All’s Well That Ends That Way
But once I put my thinking cap on, it became obvious that BIOS updates — which invariably require a restart to be applied, and another to take effect — are best handled separately from other updates. That seems to reflect recent experience with Lenovo updates too, now that I think upon the subject.
In fact, I wrote about a similar situation on March 24 in a post entitled Lenovo Vantage Updates Take Patience. Maybe I should try that thinking cap more often: it seems to work reasonably well!